Quadratic systems quiz part 1 – Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of quadratic systems with our engaging quiz part 1! This quiz will test your knowledge of quadratic equations, their solutions, and their applications. Brace yourself for a journey filled with algebraic adventures and problem-solving challenges.
Throughout this quiz, you’ll encounter a variety of questions designed to assess your understanding of the concepts covered in quadratic systems. From identifying the standard form of a quadratic equation to solving it using various methods, this quiz will put your skills to the test.
Quadratic Equations: Quadratic Systems Quiz Part 1

A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, which means it contains a variable raised to the power of 2. It generally takes the form ax2+ bx + c = 0 , where a, b, and care real numbers and ais not equal to 0.
Quadratic equations can also be written in other forms, such as:
- (x- h) 2= k (vertex form)
- y = a(x- h) 2+ k (vertex form with y-intercept)
- x2– 2px + p 2= q (completing the square form)
Standard Form
The standard form of a quadratic equation is ax2+ bx + c = 0 , where:
- ais the coefficient of the x2term and is not equal to 0.
- bis the coefficient of the xterm.
- cis the constant term.
Solving Quadratic Equations

Solving quadratic equations is a fundamental skill in algebra. Quadratic equations are equations of the form ax2+ bx + c = 0 , where a, b, and care real numbers and a ≠ 0. There are three main methods for solving quadratic equations: factoring, completing the square, and using the quadratic formula.
Tackling the intricacies of quadratic systems quiz part 1 requires a steady mind. But when the brain needs a break, why not indulge in the delectable flavors of gringo dip 54th street recipe ? Its creamy texture and zesty spices will tantalize your taste buds.
Refreshed and re-energized, return to the challenge of quadratic systems quiz part 1 with renewed focus.
Factoring, Quadratic systems quiz part 1
Factoring is the process of expressing a quadratic equation as a product of two linear factors. This method can be used when the quadratic equation can be easily factored into two binomials. For example, the equation x2– 5x + 6 = 0 can be factored as (x- 2)(x – 3) = 0 . The solutions to the equation are x = 2and x = 3.
Completing the Square
Completing the square is a method that can be used to solve any quadratic equation. It involves adding and subtracting a constant term to the equation in order to create a perfect square trinomial. For example, the equation x2+ 4x + 3 = 0 can be solved by completing the square as follows:
- Add and subtract the square of half the coefficient of the x-term, which is (4/2)2= 4 :
- Factor the perfect square trinomial:
- Solve for xby taking the square root of both sides:
x2+ 4x + 4 – 4 + 3 = 0
(x + 2)2– 1 = 0
x + 2 = ±1
x =-2 ± 1
x =-1 or x = -3
Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is a general formula that can be used to solve any quadratic equation. It is given by:
x = (-b ± √(b2
4ac)) / 2a
where a, b, and care the coefficients of the quadratic equation ax2+ bx + c = 0 . For example, the equation x2– 5x + 6 = 0 can be solved using the quadratic formula as follows:
- Substitute the values of a, b, and cinto the quadratic formula:
- Simplify the expression:
x = (-(-5) ± √((-5)2– 4(1)(6))) / 2(1)
x = (5 ± √(25- 24)) / 2
x = (5 ± 1) / 2
x = 2 or x = 3
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Methods
Each of the three methods for solving quadratic equations has its own advantages and disadvantages. Factoring is the most straightforward method, but it can only be used when the quadratic equation can be easily factored. Completing the square is a more general method, but it can be more algebraically complex than factoring.
The quadratic formula is the most general method and can be used to solve any quadratic equation, but it can be more time-consuming than factoring or completing the square.
Graphing Quadratic Functions
Quadratic functions, represented by equations in the form of y = ax^2 + bx + c, exhibit unique graphical characteristics. Understanding the relationship between these equations and their graphs is crucial for visualizing and analyzing quadratic functions.
To graph a quadratic function, several key features can be utilized:
Vertex
The vertex of a parabola, the graph of a quadratic function, represents the point where the parabola changes direction. It is the point (h, k), where h = -b/2a and k = f(h) = a(h^2) + bh + c.
Axis of Symmetry
The axis of symmetry is a vertical line that divides the parabola into two symmetrical halves. It passes through the vertex and is given by the equation x = h, where h is the x-coordinate of the vertex.
Intercepts
Quadratic functions can have two types of intercepts: x-intercepts and y-intercepts. X-intercepts are the points where the parabola crosses the x-axis, and they can be found by solving the equation y = 0. Y-intercepts are the points where the parabola crosses the y-axis, and they can be found by solving the equation x = 0.
By identifying these key features, we can accurately graph quadratic functions. For instance, if we have a quadratic function y = x^2 – 4x + 3, its vertex is (2, -1), its axis of symmetry is x = 2, and its intercepts are (3, 0) and (1, 0).
Applications of Quadratic Functions

Quadratic functions find their applications in various real-world scenarios. They are used to model and solve problems in areas like physics, engineering, and economics.
One common application is in understanding parabolic trajectories. When an object is launched into the air, its path follows a parabolic trajectory. The height of the object at any given time can be modeled using a quadratic function, which takes into account the initial velocity, launch angle, and acceleration due to gravity.
Projectile Motion
Projectile motion is a special case of parabolic trajectory where an object is launched with a certain velocity and angle, and its path is influenced by gravity. The trajectory of a projectile can be modeled using a quadratic function, which can be used to calculate the height, range, and other parameters of the motion.
Optimization Problems
Quadratic functions are also used to solve optimization problems, where the goal is to find the maximum or minimum value of a given function. This is often encountered in fields like economics and engineering, where the objective is to optimize a quantity such as profit or efficiency.
Advanced Concepts
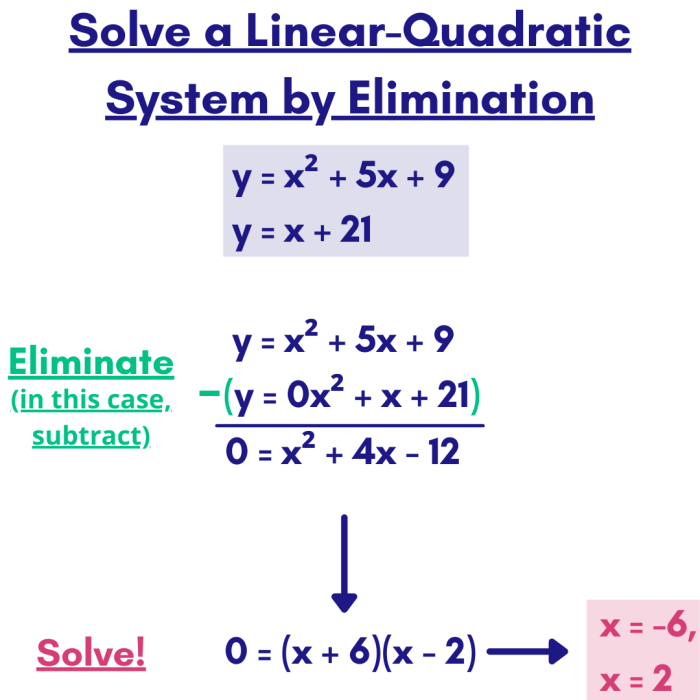
The study of quadratic equations can delve into more intricate ideas that expand our understanding of these functions.
The Discriminant
The discriminant is a crucial element in determining the nature of the roots of a quadratic equation. Represented by the symbol Δ, it is calculated using the formula Δ = b²4ac, where a, b, and c are the coefficients of the quadratic equation ax² + bx + c =
0. The discriminant provides valuable insights into the behavior of the equation
Δ > 0
The equation has two distinct real roots.
Δ = 0
The equation has one real root, which is a double root.
Δ < 0
The equation has two complex roots, which are not real numbers.
Complex Roots
Complex roots arise when the discriminant is negative. These roots are not real numbers but rather involve the imaginary unit i, which is defined as the square root of1. A complex root can be expressed in the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers.
To solve for complex roots, we use the quadratic formula, but we must consider the imaginary unit.
Quadratic Functions and Conic Sections
Quadratic functions exhibit a close relationship with conic sections, which are geometric shapes that result from the intersection of a plane with a cone. The type of conic section depends on the discriminant:
Δ > 0
Parabola
Δ = 0
Line
Δ < 0
Circle or ellipse
Understanding the discriminant and its implications allows us to delve deeper into the behavior of quadratic equations and their geometric representations.
FAQ Insights
What is the standard form of a quadratic equation?
The standard form of a quadratic equation is ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0.
How can I solve a quadratic equation by factoring?
To solve a quadratic equation by factoring, factor the left-hand side of the equation into two binomials. Set each binomial equal to zero and solve for the variable.
What is the quadratic formula?
The quadratic formula is a general formula that can be used to solve any quadratic equation: x = (-b ± √(b² – 4ac)) / 2a.