Given the reaction at equilibrium 2so2+o2 – Delving into the realm of chemical equilibrium, we examine the intriguing reaction 2SO2 + O2. This reaction serves as a cornerstone in industrial processes and environmental considerations, making it a topic of significant scientific and practical interest.
As we embark on this exploration, we will delve into the intricacies of equilibrium, unraveling the factors that influence its delicate balance. We will uncover the industrial applications of this reaction, particularly its role in sulfuric acid production, and assess its environmental implications.
Chemical Equilibrium

Chemical equilibrium is a state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products of a chemical reaction do not change over time. This means that the forward and reverse reactions are occurring at the same rate.
The conditions necessary for a reaction to reach equilibrium are:
- The reaction must be reversible.
- The system must be closed, meaning that no matter can enter or leave the system.
- The temperature must be constant.
An example of a reaction at equilibrium is the reaction between hydrogen and iodine:
H2 + I2 ⇌ 2HI
The Reaction 2SO2 + O2
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction 2SO2 + O2 is:
SO2 + O2 ⇌ 2SO3
The reactants in this reaction are SO2 and O2, and the product is SO3.
This reaction is an equilibrium reaction because it is reversible. This means that the forward and reverse reactions can both occur.
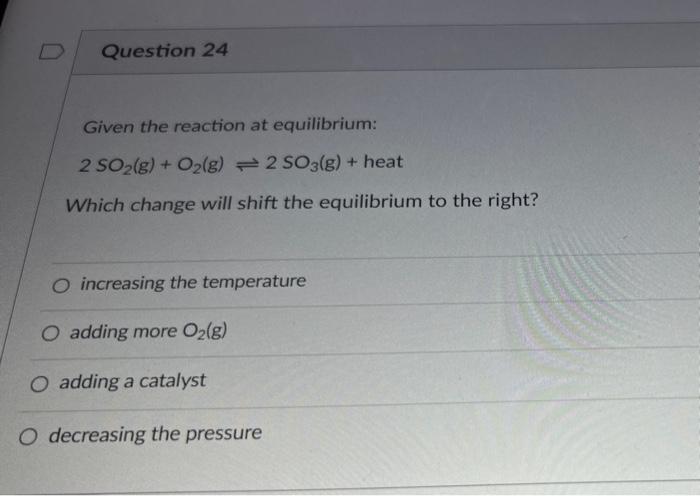
Factors Affecting the Equilibrium, Given the reaction at equilibrium 2so2+o2
The equilibrium of the reaction 2SO2 + O2 can be affected by the following factors:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Concentration
Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right, favoring the formation of SO3. Increasing the pressure also shifts the equilibrium to the right, but only if the volume of the system is decreased.
Increasing the concentration of SO2 or O2 shifts the equilibrium to the right, while increasing the concentration of SO3 shifts the equilibrium to the left.
Applications of the Reaction
The reaction 2SO2 + O2 is used industrially to produce sulfuric acid.
Sulfuric acid is a very important chemical that is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Fertilizer production
- Petroleum refining
- Metalworking
The reaction 2SO2 + O2 also has some environmental implications.
SO2 is a pollutant that can cause respiratory problems. The reaction 2SO2 + O2 helps to remove SO2 from the atmosphere, but it also produces SO3, which is another pollutant.
Advanced Concepts
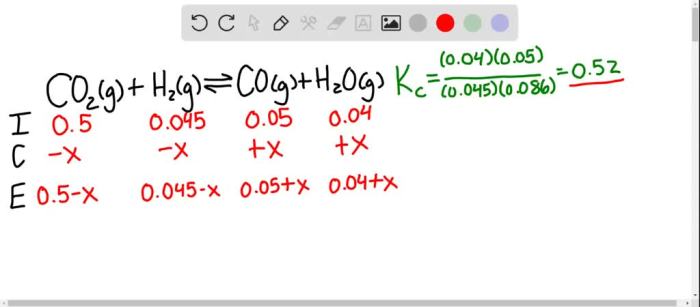
The equilibrium constant is a number that is used to predict the equilibrium position of a reaction.
The equilibrium constant for the reaction 2SO2 + O2 is:
K = [SO3]^2 / [SO2]^2[O2]
The equilibrium constant can be used to solve equilibrium problems.
For example, if we know the equilibrium constant and the concentrations of the reactants and products, we can use the equilibrium constant expression to calculate the equilibrium concentration of any of the species.
General Inquiries: Given The Reaction At Equilibrium 2so2+o2
What is the significance of the equilibrium constant in this reaction?
The equilibrium constant provides a quantitative measure of the extent to which the reaction proceeds towards completion. It allows us to predict the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products under different conditions.
How does temperature affect the equilibrium of this reaction?
Increasing temperature favors the endothermic forward reaction, leading to a decrease in the concentration of reactants and an increase in the concentration of products.
What are the environmental implications of this reaction?
The production of sulfur dioxide (SO2) from this reaction contributes to acid rain, which can damage ecosystems and infrastructure.