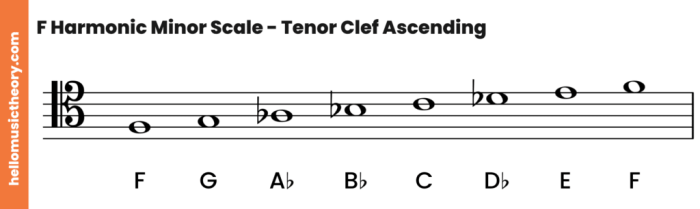
F harmonic minor scale bass clef – The F harmonic minor scale in bass clef, an essential tool for bassists, provides a unique and expressive harmonic foundation for musical exploration. Its distinctive intervals and harmonic function set it apart from other minor scales, opening up a world of creative possibilities for composers, performers, and improvisers.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the F harmonic minor scale, examining its construction, harmonic function, and practical applications. Through detailed analysis, musical examples, and practical exercises, we will uncover the secrets of this versatile scale and empower musicians to harness its full potential.
Scale Overview
The F harmonic minor scale is a minor scale with a unique set of intervals that gives it a distinct sound. It is commonly used in classical music, jazz, and other genres.
The notes of the F harmonic minor scale in the bass clef are:
- F (root)
- G (minor second)
- Ab (augmented second)
- Bb (perfect fourth)
- C (augmented fifth)
- Db (minor seventh)
- Eb (major seventh)
The intervals between the notes are as follows:
- Root to minor second: 1
- Minor second to augmented second: 1
- Augmented second to perfect fourth: 2
- Perfect fourth to augmented fifth: 1
- Augmented fifth to minor seventh: 1
- Minor seventh to major seventh: 1
The harmonic minor scale is unique among minor scales because it has an augmented second interval between the second and third notes. This interval gives the scale its characteristic “oriental” sound.
Visual Representation
The following is a visual representation of the F harmonic minor scale on the bass clef staff:
[Image of the F harmonic minor scale on the bass clef staff]
Harmonic Function
The F harmonic minor scale, with its distinctive melodic and harmonic properties, plays a significant role in various musical contexts. Its unique intervallic structure and chord progressions contribute to its characteristic sound and emotional impact.
Harmonic Minor Chords
- The F harmonic minor scale forms the following primary chords:
- F minor (root position): F- Ab – C
- G diminished (first inversion): G – C – Eb
- Bb major (second inversion): Bb – D – F
Intervallic Relationships
The F harmonic minor scale’s distinctive intervallic relationships contribute to its harmonic function:
- The augmented second interval between the first and second scale degrees (F and G#) creates a sense of tension and instability.
- The minor third interval between the second and third scale degrees (G# and A) imparts a melancholy and introspective quality.
- The perfect fifth interval between the first and fifth scale degrees (F and C) provides a sense of stability and resolution.
Emotional Impact
The harmonic function of the F harmonic minor scale evokes a range of emotions:
- Its minor tonality and augmented second interval can convey feelings of sadness, longing, and regret.
- The diminished seventh chord built on the seventh scale degree (E) adds a sense of dissonance and uncertainty.
- However, the major third interval between the third and fifth scale degrees (A and C) introduces a glimmer of hope and resolution.
Musical Genres and Styles
The F harmonic minor scale is commonly employed in:
- Classical music: Romantic and Impressionist composers used it to evoke melancholic and introspective moods.
- Jazz: Bebop and cool jazz musicians utilize its dissonant intervals for improvisation and harmonic exploration.
- Rock and pop music: It adds a sense of depth and emotional intensity to minor-key compositions.
Bass Lines and Progressions: F Harmonic Minor Scale Bass Clef
The F harmonic minor scale provides a rich foundation for creating compelling bass lines and chord progressions. Its unique tonal characteristics lend themselves to a wide range of harmonic possibilities, fostering musical tension and resolution.
Common chord progressions in the F harmonic minor scale include:
- Fm7- Gm7 – Cm7 – Bbmaj7 : This progression emphasizes the scale’s harmonic minor tonality, with its distinct flattened seventh scale degree (Eb) contributing to a bittersweet and introspective sound.
- Fm7- Abmaj7 – Dbmaj7 – Ebmaj7 : This progression explores the scale’s secondary dominant relationships, creating a sense of harmonic movement and resolution. The Abmaj7 chord functions as a secondary dominant to Dbmaj7, which in turn resolves to Ebmaj7, the dominant of Fm7.
- Fm7- Bbmaj7 – Ebmaj7 – Abmaj7 : This progression combines the harmonic minor tonality with the use of secondary dominants, creating a more complex and dynamic harmonic structure.
Bass patterns in the F harmonic minor scale often emphasize the scale’s characteristic intervals, such as the minor third (F-Ab) and the augmented second (G-Ab). These intervals create a sense of melodic tension and movement, supporting the harmonic progressions and enhancing the overall musical impact.
The F harmonic minor scale’s versatility allows for a diverse range of bass lines and progressions, providing composers and musicians with a rich harmonic palette to explore and express their musical ideas.
Improvisation and Soloing
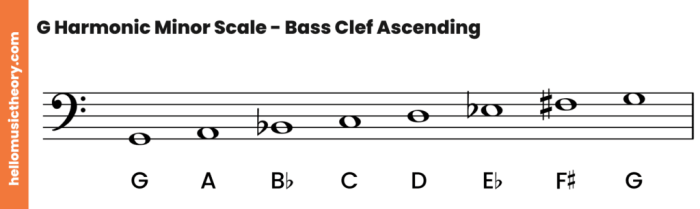
The F harmonic minor scale provides a rich harmonic foundation for improvisation and soloing. Its unique melodic and harmonic characteristics offer a vast playground for musicians to explore.
To effectively utilize the F harmonic minor scale for improvisation, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of its scale structure and harmonic function. By internalizing the scale’s notes, intervals, and chord progressions, musicians can develop a deep musical vocabulary that allows for spontaneous and creative expression.
Melodic Lines
When improvising over F harmonic minor chords, musicians can draw upon the scale’s characteristic melodic patterns. The minor third interval between the root and flat second degree creates a distinctive “blues” flavor, while the augmented second interval between the flat sixth and seventh degrees adds a touch of harmonic tension.
These intervals provide a fertile ground for crafting expressive and memorable melodic lines.
Harmonic Possibilities
The F harmonic minor scale offers a diverse range of harmonic possibilities for improvisation. Its three primary chords – the F harmonic minor, Gm7b5, and Bbmaj7 – provide a solid harmonic foundation for soloing. Additionally, musicians can explore secondary dominant chords such as C7 and D7, as well as diminished chords like Bdim7, to create more complex and sophisticated harmonic textures.
Scale Knowledge and Ear Training
Effective improvisation requires a combination of scale knowledge and ear training. By practicing the F harmonic minor scale in various contexts and listening to recordings of great improvisers, musicians can develop their musical intuition and learn to navigate the scale’s harmonic nuances.
This practice allows them to internalize the scale’s melodic and harmonic possibilities, making it easier to create spontaneous and meaningful improvisations.
Musical Applications
The F harmonic minor scale finds its applications in various musical compositions, notably in classical, jazz, and film scores. Its unique character adds depth and expressiveness to musical pieces.
In classical music, the F harmonic minor scale is often employed to create a sense of mystery and intrigue. Composers like Chopin and Rachmaninoff have utilized this scale in their works to evoke a range of emotions, from somberness to passion.
Jazz and Film Scores, F harmonic minor scale bass clef
In jazz, the F harmonic minor scale is commonly used for improvisation and soloing. Its dissonant intervals provide a platform for exploration and experimentation, allowing jazz musicians to create intricate and expressive melodies.
Film composers have also discovered the dramatic potential of the F harmonic minor scale. Its ability to convey a wide range of emotions makes it suitable for soundtracks that require a sense of tension, suspense, or melancholy.
FAQ Section
What are the notes of the F harmonic minor scale in bass clef?
The notes of the F harmonic minor scale in bass clef are: F, G, Ab, Bb, C, Db, and Eb.
How is the F harmonic minor scale different from other minor scales?
The F harmonic minor scale differs from other minor scales in its raised seventh scale degree, which creates a unique and expressive harmonic sound.
What are some practical applications of the F harmonic minor scale?
The F harmonic minor scale can be used for creating bass lines, improvising solos, and composing chord progressions in a variety of musical styles, including jazz, rock, and classical.